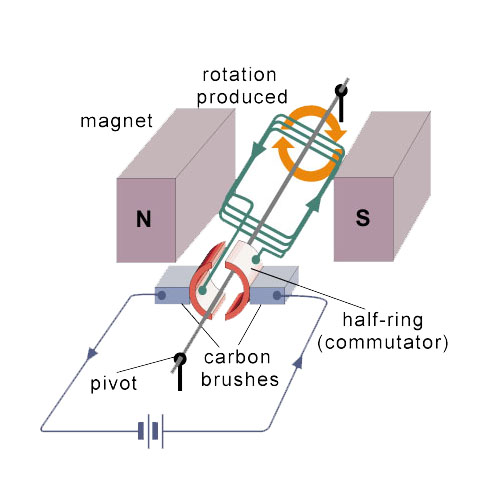
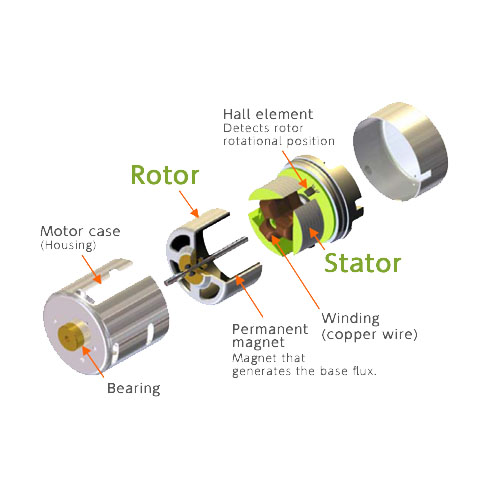
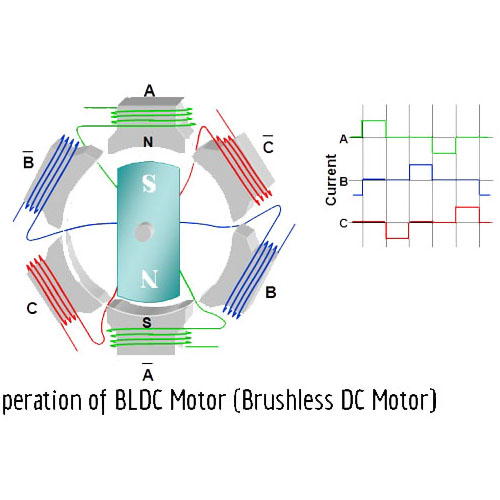
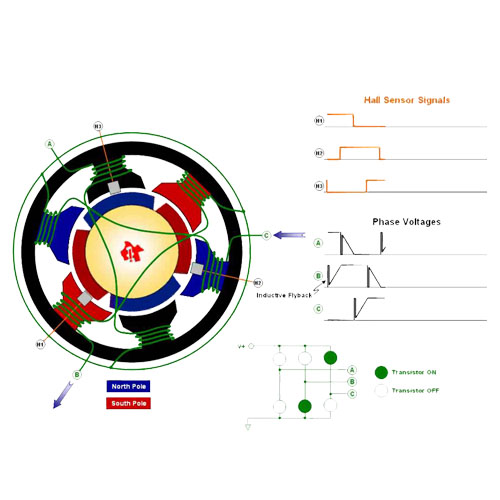
DC electric motors
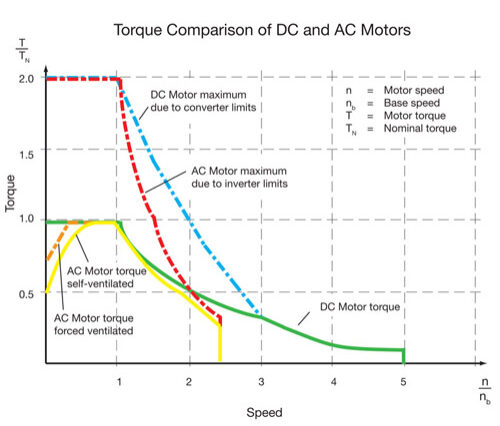
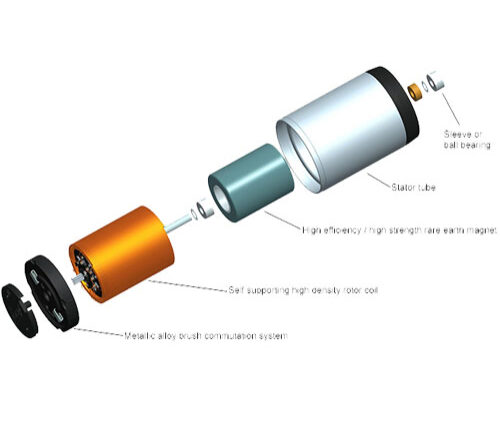
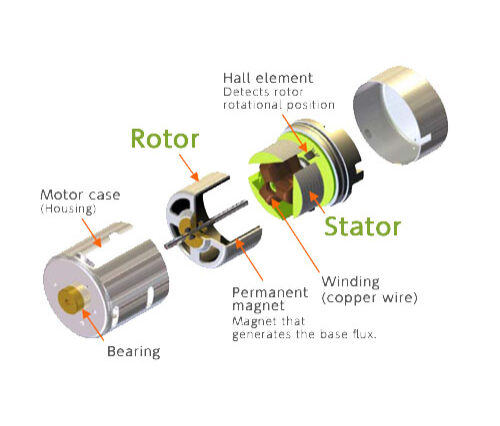
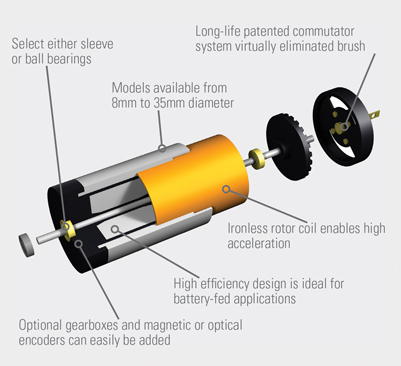
DC electric motors There are three types of electrical connections between the stator and rotor possible for DC electric motors: series, shunt/parallel and compound (various blends of series and shunt/parallel) and each has unique speed/torque characteristics appropriate for different loading torque profiles/signatures.